Lung cancer is the predominant cause of cancer related deaths. Within the main types of lung cancers, small cell lung cancer (SCLC) and non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), NSCLC accounts for approximately 85%, with a poor 5-year survival of only ~15%. Despite the significant progress in treatment options, prognosis remains poor because of the locally advanced metastatic tumors in most patients at the time of diagnosis. A team of scientists from Kunming Institute of Zoology, Chinese Academy of Sciences (KIZ, CAS), recently found that Progestin and AdipoQ Receptor 4 (PAQR4) promotes chemoresistance in NSCLC through inhibiting nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) protein degradation, which provides PAQR4 as a potential novel biomarker and therapeutic target for non-small cell lung cancer. The authors provided evidence showing that PAQR4 is increased in NSCLC patients and cancer cell lines, and identified many mutations in PAQR4 in non-small cell lung cancer tissues. They demonstrated that PAQR4 high expression correlates with worse clinical outcomes, and that its down-regulation suppresses cell proliferation by triggering cellular apoptosis. Importantly, PAQR4 physically interacts with Nrf2, blocks the interaction between Nrf2 and Keap1 (Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1), and thus Nrf2 is stably expressed and accumulated in the nucleus, which activates the expression of a series of genes involved in antioxidant stress.
This study has identified a new mechanism by which PAQR4 regulates the ubiquitination and protein stability of transcription factor Nrf2, suggesting that screening and applying leading compounds that specifically inhibit PAQR4 functions, in combination with chemotherapy drugs, may lead to better clinical efficacy in future.
This work was published in Theranostics (doi: 10.7150/thno.43142). XU Peifang (Master student at KIZ and University of Science and Technology of China), Dr. JIANG Liping (Associate Investigator at KIZ) and YANG Yang (Department of Thoracic Surgery, the First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University) are co-first authors of this work. Dr. CHEN Yongbin (Investigator at KIZ) and Dr. YANG Cuiping (Investigator at KIZ) are co-corresponding authors. This work was supported by grants from National Key Research and Development Program of China, Stem Cell and Translational Research, National Nature Science Foundation of China, Yunnan Applied Basic Research Projects.
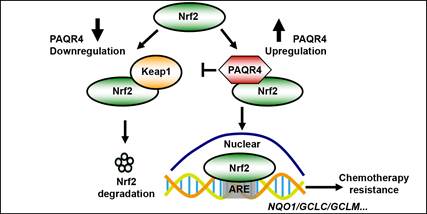
PAQR4 promotes chemotherapy resistance mediated by Nrf2 (Image by CHEN Yongbin)
(By CHEN Yongbin; Editor: HE Linxi)
Contact:
HE Linxi
helinxi@mail.kiz.ac.cn
